transformation p o r n|rn to rm transformation matrix : Tuguegarao Determine if a linear transformation is onto or one to one. Let T: Rn ↦ Rm be a linear transformation. We define the range or image of T as the set of vectors of Rm . Resultado da 10 de dez. de 2023 · Quieres agua video original 'sem tapar': la grabación viral de un payaso sicario en México. El video conocido como 'Quieres .
0 · rn to rm transformation matrix
1 · rn to rm transformation
2 · r n to r m linear transformation
3 · one to one transformation pdf
4 · one to one transformation formula
5 · one to one transformation
6 · linear transformation from rn to r
7 · More
8 · 1 to onto transformation
Resultados animalitos hoy Lunes 26-02-2024, Tu azar, tuaza.
transformation p o r n*******Let \(T: \mathbb{R}^n \mapsto \mathbb{R}^m\) be a linear transformation. Then there are some important properties of \(T\) which will be examined in this section.
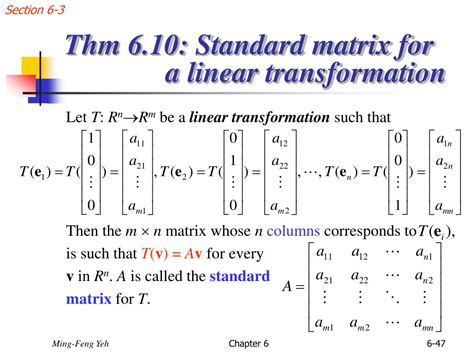
Find a linear transformation T from R3 to R4 such that the null space N(T) = {0} and the range R(T) = V. Describe T by its matrix A . Let u = [1 1 0] and T: R3 → R3 be the linear . Determine if a linear transformation is onto or one to one. Let T: Rn ↦ Rm be a linear transformation. We define the range or image of T as the set of vectors of Rm . These linear transformations are probably different from what your teacher is referring to; while the transformations presented in this video are functions that associate vectors with vectors, your teacher's transformations likely refer to actual .Objectives. Learn how to verify that a transformation is linear, or prove that a transformation is not linear. Understand the relationship between linear . Let T: Rn ↦ Rm be a linear transformation. Then the matrix A satisfying T(→x) = A→x is given by A = [ | | T(→e1) ⋯ T(→en) | |] where →ei is the ith column of .Two examples of linear transformations T :R2 → R2 are rotations around the origin and reflections along a line through the origin. An example of a linear transformation T :P .
The simple answer is that the matrix will be m x n where the domain is R^n and the codomain is R^m. The size of a matrix is written m rows by n columns, usually expressed as m x n. For a linear transformation T(x) from R^n (domain) to R^m .
392 Linear Transformations. 7.3 Isomorphisms and Composition. nderlying space displayed in dif. R2 = {(a, b) | a, b ∈ R} and P1 = {a + bx | a, b ∈ R} Compare the .transformation p o r nLinear Transformation. transformation T : Rm → Rn is called a linear transformation if, for every scalar. and every pair of vectors u and v in Rm. T (u + v) = T (u) + T (v) and. T (cu) .Fact: If T: Rk!Rnand S: Rn!Rmare both linear transformations, then S Tis also a linear transformation. Question: How can we describe the matrix of the linear transformation S T in terms of the matrices of Sand T? Fact: Let T: Rn!Rn and S: Rn!Rm be linear transformations with matrices Band A, respectively. Then the matrix of S Tis the .
Show that the differentiation and integration operations on Pn are linear transformations. More precisely, D:Pn →Pn−1 where D[p(x)]=p′(x)for all p(x)in Pn I :Pn →Pn+1 where I[p(x)]= Zx 0 p(t)dt for all p(x)in Pn are linear transformations. Solution. These restate the followingfundamental properties of differentiation and integration.386 Linear Transformations Theorem 7.2.3 LetA be anm×n matrix, and letTA:Rn →Rm be the linear transformation induced byA, that is TA(x)=Axfor all columnsxinRn. 1. TA is onto if and only ifrank A=m. 2. TA is one-to-one if and only ifrank A=n. Proof. 1. We have that im TA is the column space of A (see Example 7.2.2), so TA is onto if and only if the column .
matrices O n also form a subgroup of M n. Note that the composition of an orthogonal matrix with a translation is. A t # » Clearly, translations, which are isomorphic to (R. n b b + = t #» A, b. Ab. since. A(x + b) = Ax + Ab. In particular, a translation and an orthogonal matrix do not commute with each other. Consider the projection. π :M . Here, for the first time we directly observe a complete transformation from p- to n-type perovskite surface energetics by a defect-passivating process using a nature molecule, capsaicin (Figure 1 A). We attribute the effect to a spontaneous p-n homojunction formation in the perovskite active layer. We observe an improved charge transport and a .Two examples of linear transformations T :R2 → R2 are rotations around the origin and reflections along a line through the origin. An example of a linear transformation T :P n → P n−1 is the derivative function that maps each polynomial p(x)to its derivative p′(x). As we are going to show, every linear transformation T :Rn → Rm isParity (physics) In physics, a parity transformation (also called parity inversion) is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it can also refer to the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates (a point reflection ): It can also be thought of as a test for chirality of a physical phenomenon, in .
Transformations in math involve changing a shape's position or which way the shape points. There are three main types: translations (moving the shape), rotations (turning the shape), and reflections (flipping the shape like a mirror image). Rigid .
Solution. First, we have just seen that T(→v) = proj→u(→v) is linear. Therefore by Theorem 5.2.1, we can find a matrix A such that T(→x) = A→x. The columns of the matrix for T are defined above as T(→ei). It follows that T(→ei) = proj→u(→ei) gives the ith column of the desired matrix.transformation p o r n rn to rm transformation matrix8 years ago. STEP 1: Imagine that "orange" dot (that tool that you were playing with) is on top of point P. STEP 2: Point Q will be the point that will move clockwise or counter clockwise. STEP 3: When you move point Q to point R, you have moved it by 90 degrees counter clockwise (can you visualize angle QPR as a 90 degree angle?).After transformation, the residuals from the ANOVA are closer to a normal distribution—although not perfectly—, making the F-test more appropriate. In addition, the test is more powerful as indicated by the lower p-value (p = 0.005) than with the untransformed data. The plot of the residuals vs. the fitted values shows that the .n(u n x) = u 1u T 1 + + u nu T n x: Hence proj V x = 2 6 4 jj j u 1 u 2 u n jj j 3 7 5 2 6 6 4 Tu 1 uT..2. Tu n 3 7 7 5x We have hence found a matrix formula for the orthogonal projection: P= QQT; where Q= 2 6 4 jj j u 1 u 2 u n jj j 3 7 5 Another important class of matrices are the symmetric matrices satisfying AT = A. Note that it follows .
Theorem(One-to-one matrix transformations) Let A be an m × n matrix, and let T ( x )= Ax be the associated matrix transformation. The following statements are equivalent: T is one-to-one. For every b in R m , the equation T ( x )= b has at most one solution. For every b in R m , the equation Ax = b has a unique solution or is inconsistent.O is the origin and P is the point (1, -2). R y and R x are reflections around the x - and y -axes. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A product transformation multiplies coordinates to transform the image., Click on the following figure to show the reflection about m .After transformation, the residuals from the ANOVA are closer to a normal distribution—although not perfectly—, making the F-test more appropriate. In addition, the test is more powerful as indicated by the lower p-value .
n(u n x) = u 1u T 1 + + u nu T n x: Hence proj V x = 2 6 4 jj j u 1 u 2 u n jj j 3 7 5 2 6 6 4 Tu 1 uT..2. Tu n 3 7 7 5x We have hence found a matrix formula for the orthogonal projection: P= QQT; where Q= 2 6 4 jj j u 1 u 2 u n jj j 3 7 5 Another important class of matrices are the symmetric matrices satisfying AT = A. Note that it follows .Theorem(One-to-one matrix transformations) Let A be an m × n matrix, and let T ( x )= Ax be the associated matrix transformation. The following statements are equivalent: T is one-to-one. For every b in R m , the equation T ( x )= b has at most one solution. For every b in R m , the equation Ax = b has a unique solution or is inconsistent.
O is the origin and P is the point (1, -2). R y and R x are reflections around the x - and y -axes. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A product transformation multiplies coordinates to transform the image., Click on the following figure to show the reflection about m .rn to rm transformation matrixLinear Algebra Proof. Suppose vectors v 1 ,. v p span R n, and let T: R n -> R n be a linear transformation. Suppose T (v i) = 0 for i =1, ., p. Show that T is a zero transformation. That is, show that if x is any vector in R n, then T (x) = 0. Be sure to include definitions when needed and cite theorems or definitions for each step along .

(a) What are the two defining properties of a linear transformation? (b) Let T: R n → R m and U: R n → R m be two linear transformations. Define a new linear transformation P: R n → R m by P (x) = T (x) + U (x) for any x in R n. Prove that P is linear or that P is not linear. A rigid transformation (also known as an isometry or congruence transformation) is a transformation that does not change the size or shape of a figure. The new figure created by a transformation is called the image. The original figure is called the preimage. There are three rigid transformations: translations, reflections, and .
2.6 Linear Transformations If A is an m×n matrix, recall that the transformation TA:Rn →Rm defined by TA(x)=Ax for all x in Rn is called the matrix transformation induced by A. In Section 2.2, we saw that many important geometric transformations were in fact matrix transformations. These transformations can be characterized in a differentway. Richter transformation is a devastating and rare but not uncommon development of an aggressive B-cell lymphoma in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Prognosis is dismal, with survival generally in the realm of months to a couple of years. . Jain, N., & O'Brien, S. (2018). Clinical evaluation .Prove that a linear transformation P: V → V P: V → V of a finite dimensional vector space satisfies P2 = P P 2 = P if and only if there exists a basis with respect to which P P can be written as a block matrix. P = [I 0 0 0]. P = [ I 0 0 0]. Hence determine the minimal and characteristic polynomials of P P.There are three easy tests to check if a transformation is canonical. Note that some multiplicative constants might pop up in certain textbooks, depending on the exact definition of canonical transformation.C. We have an expert-written solution to this problem! all side lengths of JKL equal 2 units. a transformation maps JKL to J'K'L. the length of side J'K' is 5 units. is this a rigid transformaiton? B. A rigid transformation can also be referred to as an isometric transformation. The prefix "iso-" means "of the same" and "-metric" means "measure."
web26 de jun. de 2018 · Localizado na Praia de Pipa (RN), o espaço oferece massagens estimulantes, bar, piscina, boate, DJs e passeios pela .
transformation p o r n|rn to rm transformation matrix